注意
前往結尾以下載完整範例程式碼。
累積分佈#
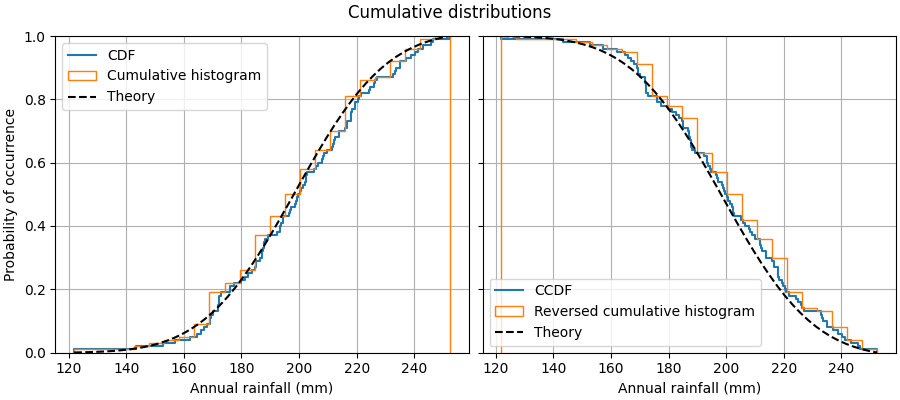
此範例顯示如何繪製樣本的經驗累積分佈函數 (ECDF)。我們也顯示理論 CDF。
在工程中,ECDF 有時稱為「不超過」曲線:給定 x 值的 y 值表示樣本中觀測值低於該 x 值的機率。例如,x 軸上的值 220 對應於 y 軸上的約 0.80,因此樣本中的觀測值不超過 220 的機率為 80%。相反地,經驗互補累積分佈函數(ECCDF 或「超過」曲線)顯示樣本中觀測值高於值 x 的機率 y。
繪製 ECDF 的直接方法是 Axes.ecdf。傳遞 complementary=True 會產生 ECCDF。
或者,可以使用 ax.hist(data, density=True, cumulative=True) 先將資料分箱,如同繪製直方圖一樣,然後計算並繪製每個分箱中項目頻率的累積總和。在這裡,若要繪製 ECCDF,請傳遞 cumulative=-1。請注意,此方法會產生 E(C)CDF 的近似值,而 Axes.ecdf 是精確的。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(19680801)
mu = 200
sigma = 25
n_bins = 25
data = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, size=100)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(9, 4), layout="constrained")
axs = fig.subplots(1, 2, sharex=True, sharey=True)
# Cumulative distributions.
axs[0].ecdf(data, label="CDF")
n, bins, patches = axs[0].hist(data, n_bins, density=True, histtype="step",
cumulative=True, label="Cumulative histogram")
x = np.linspace(data.min(), data.max())
y = ((1 / (np.sqrt(2 * np.pi) * sigma)) *
np.exp(-0.5 * (1 / sigma * (x - mu))**2))
y = y.cumsum()
y /= y[-1]
axs[0].plot(x, y, "k--", linewidth=1.5, label="Theory")
# Complementary cumulative distributions.
axs[1].ecdf(data, complementary=True, label="CCDF")
axs[1].hist(data, bins=bins, density=True, histtype="step", cumulative=-1,
label="Reversed cumulative histogram")
axs[1].plot(x, 1 - y, "k--", linewidth=1.5, label="Theory")
# Label the figure.
fig.suptitle("Cumulative distributions")
for ax in axs:
ax.grid(True)
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel("Annual rainfall (mm)")
ax.set_ylabel("Probability of occurrence")
ax.label_outer()
plt.show()
參考文獻
本範例中顯示下列函數、方法、類別和模組的使用
腳本的總執行時間:(0 分鐘 1.604 秒)