注意
前往結尾以下載完整的範例程式碼。
pcolormesh#
axes.Axes.pcolormesh 可讓您產生 2D 影像樣式的繪圖。請注意,它比類似的 pcolor 快。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import BoundaryNorm
from matplotlib.ticker import MaxNLocator
基本 pcolormesh#
我們通常透過定義四邊形的邊緣和四邊形的值來指定 pcolormesh。請注意,在這裡 *x* 和 *y* 在各自的維度中比 Z 多一個元素。
np.random.seed(19680801)
Z = np.random.rand(6, 10)
x = np.arange(-0.5, 10, 1) # len = 11
y = np.arange(4.5, 11, 1) # len = 7
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.pcolormesh(x, y, Z)
非線性 pcolormesh#
請注意,我們也可以為 *X* 和 *Y* 指定矩陣,並且具有非線性四邊形。
置中座標#
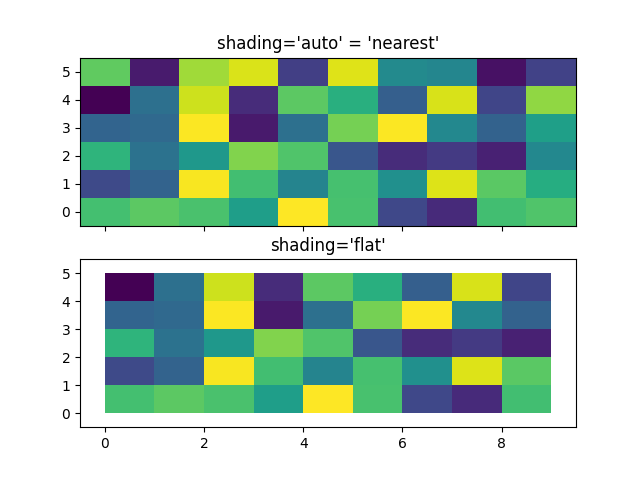
通常,使用者希望將與 *Z* 相同大小的 *X* 和 *Y* 傳遞給 axes.Axes.pcolormesh。如果傳遞了 shading='auto'(由 rcParams["pcolor.shading"] (預設值:'auto')設定的預設值),這也是允許的。在 Matplotlib 3.3 之前,shading='flat' 會捨棄 *Z* 的最後一欄和一列,但現在會產生錯誤。如果這真的是您想要的,請手動捨棄 Z 的最後一列和一欄
x = np.arange(10) # len = 10
y = np.arange(6) # len = 6
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True, sharey=True)
axs[0].pcolormesh(X, Y, Z, vmin=np.min(Z), vmax=np.max(Z), shading='auto')
axs[0].set_title("shading='auto' = 'nearest'")
axs[1].pcolormesh(X, Y, Z[:-1, :-1], vmin=np.min(Z), vmax=np.max(Z),
shading='flat')
axs[1].set_title("shading='flat'")
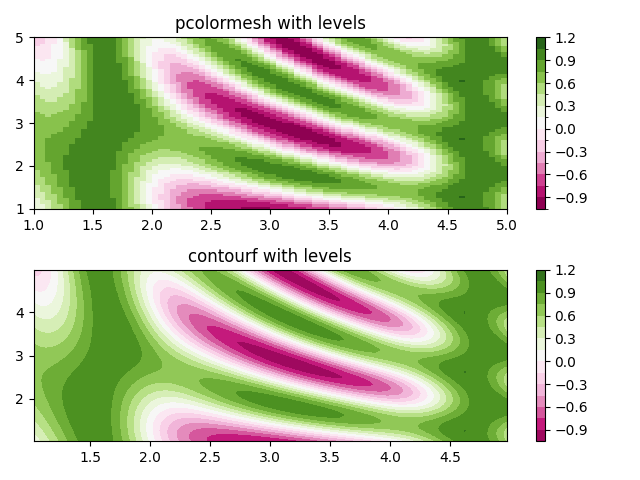
使用 Norm 建立水平#
示範如何組合正規化和色彩映射實例,以在 axes.Axes.pcolor、axes.Axes.pcolormesh 和 axes.Axes.imshow 類型繪圖中繪製「水平」,其方式與 contour/contourf 的水平關鍵字引數類似。
# make these smaller to increase the resolution
dx, dy = 0.05, 0.05
# generate 2 2d grids for the x & y bounds
y, x = np.mgrid[slice(1, 5 + dy, dy),
slice(1, 5 + dx, dx)]
z = np.sin(x)**10 + np.cos(10 + y*x) * np.cos(x)
# x and y are bounds, so z should be the value *inside* those bounds.
# Therefore, remove the last value from the z array.
z = z[:-1, :-1]
levels = MaxNLocator(nbins=15).tick_values(z.min(), z.max())
# pick the desired colormap, sensible levels, and define a normalization
# instance which takes data values and translates those into levels.
cmap = plt.colormaps['PiYG']
norm = BoundaryNorm(levels, ncolors=cmap.N, clip=True)
fig, (ax0, ax1) = plt.subplots(nrows=2)
im = ax0.pcolormesh(x, y, z, cmap=cmap, norm=norm)
fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax0)
ax0.set_title('pcolormesh with levels')
# contours are *point* based plots, so convert our bound into point
# centers
cf = ax1.contourf(x[:-1, :-1] + dx/2.,
y[:-1, :-1] + dy/2., z, levels=levels,
cmap=cmap)
fig.colorbar(cf, ax=ax1)
ax1.set_title('contourf with levels')
# adjust spacing between subplots so `ax1` title and `ax0` tick labels
# don't overlap
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
參考資料
此範例中顯示了以下函式、方法、類別和模組的使用方式
腳本總執行時間:(0 分 3.622 秒)