注意
跳到結尾以下載完整的範例程式碼。
繪製影像的多種方式#
在 Matplotlib 中繪製影像最常見的方式是使用 imshow。以下範例示範 imshow 的許多功能以及您可以建立的許多影像。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.cbook as cbook
import matplotlib.cm as cm
from matplotlib.patches import PathPatch
from matplotlib.path import Path
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
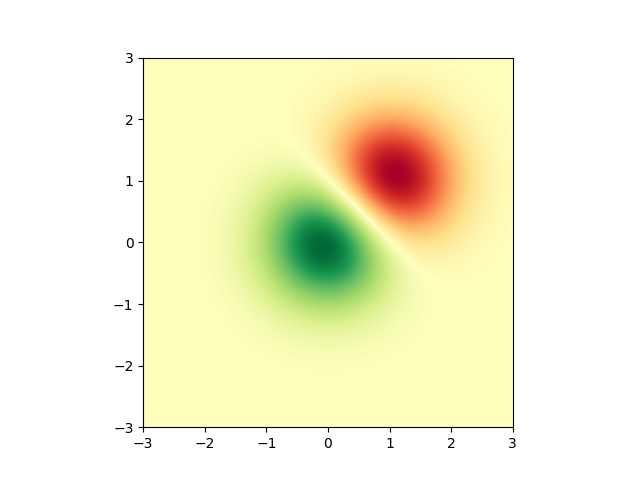
首先,我們將產生一個簡單的二元常態分佈。
delta = 0.025
x = y = np.arange(-3.0, 3.0, delta)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
Z1 = np.exp(-X**2 - Y**2)
Z2 = np.exp(-(X - 1)**2 - (Y - 1)**2)
Z = (Z1 - Z2) * 2
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
im = ax.imshow(Z, interpolation='bilinear', cmap=cm.RdYlGn,
origin='lower', extent=[-3, 3, -3, 3],
vmax=abs(Z).max(), vmin=-abs(Z).max())
plt.show()
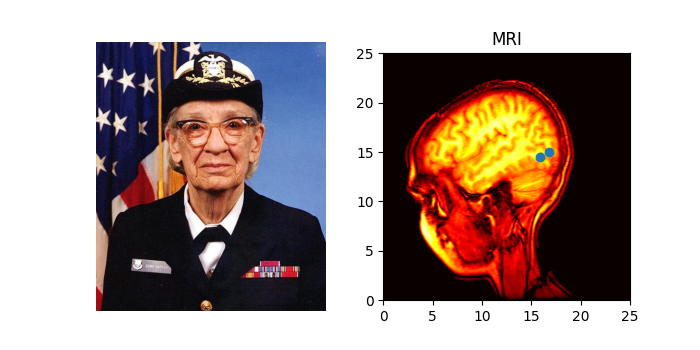
也可以顯示圖片的影像。
# A sample image
with cbook.get_sample_data('grace_hopper.jpg') as image_file:
image = plt.imread(image_file)
# And another image, using 256x256 16-bit integers.
w, h = 256, 256
with cbook.get_sample_data('s1045.ima.gz') as datafile:
s = datafile.read()
A = np.frombuffer(s, np.uint16).astype(float).reshape((w, h))
extent = (0, 25, 0, 25)
fig, ax = plt.subplot_mosaic([
['hopper', 'mri']
], figsize=(7, 3.5))
ax['hopper'].imshow(image)
ax['hopper'].axis('off') # clear x-axis and y-axis
im = ax['mri'].imshow(A, cmap=plt.cm.hot, origin='upper', extent=extent)
markers = [(15.9, 14.5), (16.8, 15)]
x, y = zip(*markers)
ax['mri'].plot(x, y, 'o')
ax['mri'].set_title('MRI')
plt.show()
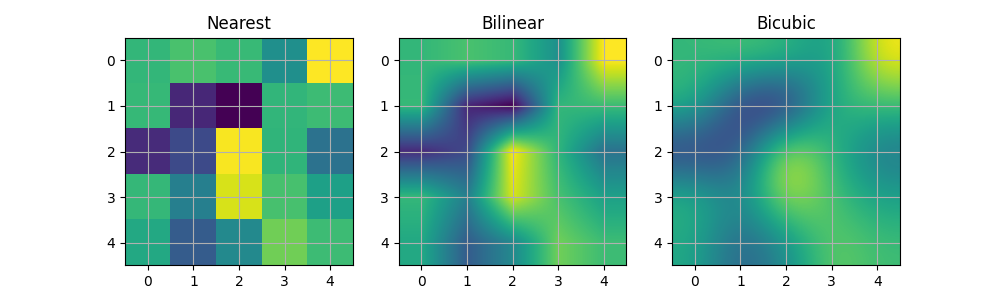
內插影像#
也可以在顯示影像之前內插影像。請小心,因為這可能會操縱資料的外觀,但它有助於達到您想要的外觀。以下我們將顯示使用三種不同內插方法內插的相同(小)陣列。
A[i, j] 處像素的中心繪製在 (i+0.5, i+0.5)。如果您使用 interpolation='nearest',則由 (i, j) 和 (i+1, j+1) 界定的區域將具有相同的顏色。如果您使用內插,則像素中心將具有與最鄰近像素相同的顏色,但其他像素將在相鄰像素之間內插。
為了防止在進行內插時出現邊緣效應,Matplotlib 會在邊緣周圍用相同的像素填充輸入陣列:如果您有一個 5x5 陣列,其中顏色如下所示,a-y
Matplotlib 會在填充陣列上計算內插和調整大小
然後擷取結果的中心區域。(極舊版本的 Matplotlib (<0.63) 不會填充陣列,而是調整視圖限制以隱藏受影響的邊緣區域。)
這種方法允許繪製陣列的完整範圍而沒有邊緣效應,例如以不同的內插方法將多個不同大小的影像分層在彼此之上 - 請參閱使用 alpha 混合分層影像。它也意味著效能損失,因為必須建立這個新的臨時填充陣列。複雜的內插也意味著效能損失;為了獲得最大效能或非常大的影像,建議使用 interpolation='nearest'。
A = np.random.rand(5, 5)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10, 3))
for ax, interp in zip(axs, ['nearest', 'bilinear', 'bicubic']):
ax.imshow(A, interpolation=interp)
ax.set_title(interp.capitalize())
ax.grid(True)
plt.show()
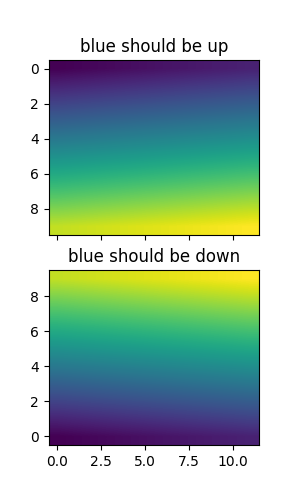
您可以透過使用 origin 參數,指定是否應使用陣列原點 x[0, 0] 在左上角或右下角繪製影像。您也可以在您的 matplotlibrc 檔案中控制預設設定 image.origin。如需有關此主題的更多資訊,請參閱有關原點和範圍的完整指南。
x = np.arange(120).reshape((10, 12))
interp = 'bilinear'
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=2, sharex=True, figsize=(3, 5))
axs[0].set_title('blue should be up')
axs[0].imshow(x, origin='upper', interpolation=interp)
axs[1].set_title('blue should be down')
axs[1].imshow(x, origin='lower', interpolation=interp)
plt.show()
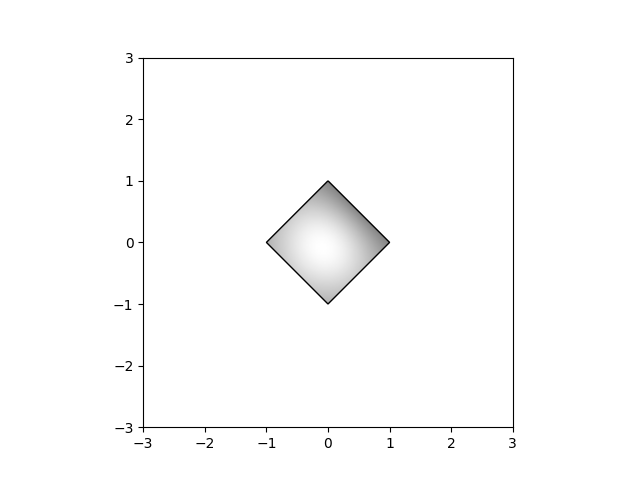
最後,我們將使用剪輯路徑顯示影像。
delta = 0.025
x = y = np.arange(-3.0, 3.0, delta)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
Z1 = np.exp(-X**2 - Y**2)
Z2 = np.exp(-(X - 1)**2 - (Y - 1)**2)
Z = (Z1 - Z2) * 2
path = Path([[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0], [0, 1]])
patch = PathPatch(path, facecolor='none')
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.add_patch(patch)
im = ax.imshow(Z, interpolation='bilinear', cmap=cm.gray,
origin='lower', extent=[-3, 3, -3, 3],
clip_path=patch, clip_on=True)
im.set_clip_path(patch)
plt.show()
參考
此範例中顯示了以下函式、方法、類別和模組的使用
腳本的總執行時間:(0 分鐘 5.518 秒)