注意
前往結尾以下載完整的範例程式碼。
緊湊佈局指南#
如何使用 tight-layout 將繪圖乾淨地放入圖形中。
tight_layout 會自動調整子圖參數,使子圖適合圖形區域。這是一個實驗性功能,可能不適用於某些情況。它只檢查刻度標籤、軸標籤和標題的範圍。
tight_layout 的替代方案是 constrained_layout。
簡單範例#
使用預設的軸定位,軸標題、軸標籤或刻度標籤有時可能會超出圖形區域,因此會被裁剪。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.rcParams['savefig.facecolor'] = "0.8"
def example_plot(ax, fontsize=12):
ax.plot([1, 2])
ax.locator_params(nbins=3)
ax.set_xlabel('x-label', fontsize=fontsize)
ax.set_ylabel('y-label', fontsize=fontsize)
ax.set_title('Title', fontsize=fontsize)
plt.close('all')
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
example_plot(ax, fontsize=24)
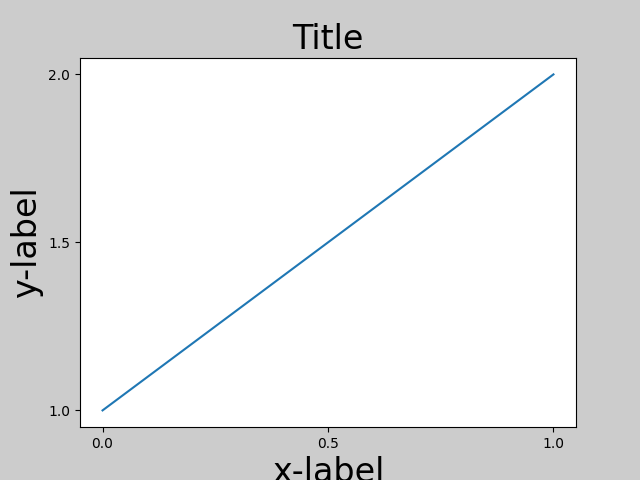
為了避免這種情況,需要調整軸的位置。對於子圖,可以使用 Figure.subplots_adjust 手動調整子圖參數。 Figure.tight_layout 會自動執行此操作。
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
example_plot(ax, fontsize=24)
plt.tight_layout()
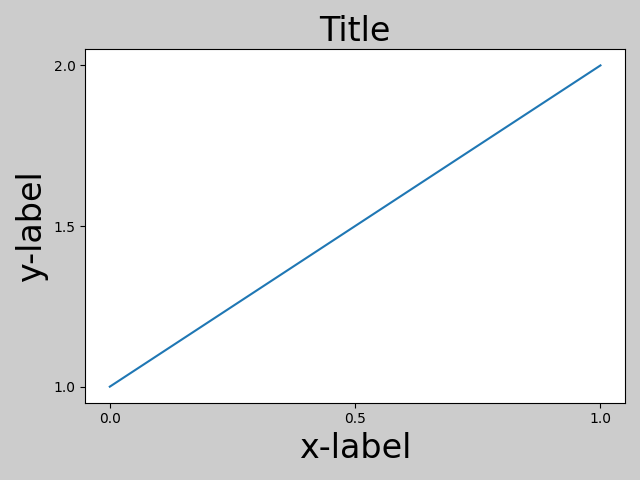
請注意,matplotlib.pyplot.tight_layout() 只會在呼叫時調整子圖參數。為了在每次重繪圖形時執行此調整,您可以呼叫 fig.set_tight_layout(True),或者等效地將 rcParams["figure.autolayout"] (預設值: False) 設為 True。
當您有多個子圖時,您經常會看到不同軸的標籤互相重疊。
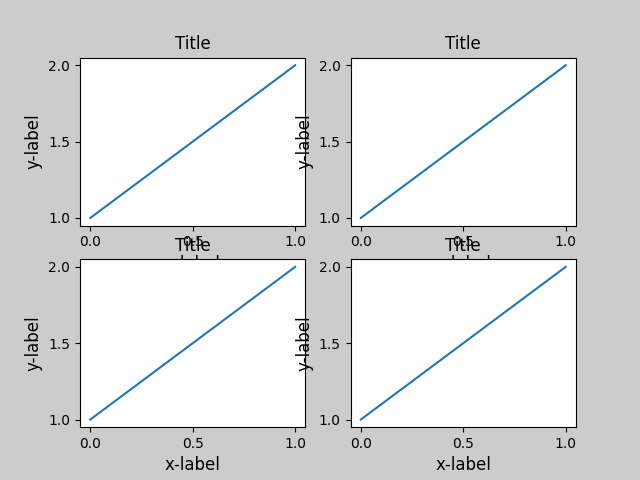
tight_layout() 也會調整子圖之間的間距,以盡量減少重疊。
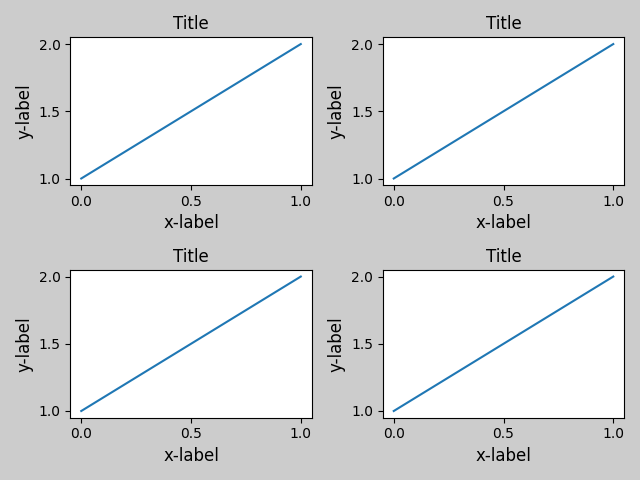
tight_layout() 可以採用 pad、w_pad 和 h_pad 的關鍵字參數。這些參數控制圖形邊框周圍和子圖之間的額外間距。間距以字體大小的分數指定。
tight_layout() 即使子圖的大小不同,只要它們的網格規格相容,也可以正常運作。在下面的範例中,ax1 和 ax2 是一個 2x2 網格的子圖,而 ax3 是一個 1x2 網格的子圖。
plt.close('all')
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = plt.subplot(221)
ax2 = plt.subplot(223)
ax3 = plt.subplot(122)
example_plot(ax1)
example_plot(ax2)
example_plot(ax3)
plt.tight_layout()
它適用於使用 subplot2grid() 建立的子圖。一般而言,從 gridspec (在圖形中排列多個軸) 建立的子圖都可以正常運作。
plt.close('all')
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = plt.subplot2grid((3, 3), (0, 0))
ax2 = plt.subplot2grid((3, 3), (0, 1), colspan=2)
ax3 = plt.subplot2grid((3, 3), (1, 0), colspan=2, rowspan=2)
ax4 = plt.subplot2grid((3, 3), (1, 2), rowspan=2)
example_plot(ax1)
example_plot(ax2)
example_plot(ax3)
example_plot(ax4)
plt.tight_layout()
雖然尚未徹底測試,但它似乎適用於 aspect != "auto" 的子圖(例如,帶有影像的軸)。
arr = np.arange(100).reshape((10, 10))
plt.close('all')
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 4))
ax = plt.subplot()
im = ax.imshow(arr, interpolation="none")
plt.tight_layout()
注意事項#
tight_layout預設會考慮軸上的所有藝術家。若要從佈局計算中移除藝術家,您可以呼叫Artist.set_in_layout。tight_layout假設藝術家所需的額外空間與軸的原始位置無關。這通常是正確的,但在極少數情況下並非如此。pad=0可能會將一些文字裁剪幾個像素。這可能是錯誤或目前演算法的限制,目前尚不清楚原因。同時,建議使用大於 0.3 的 pad。
與 GridSpec 一起使用#
GridSpec 有自己的 GridSpec.tight_layout 方法 (pyplot api pyplot.tight_layout 也適用)。
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
plt.close('all')
fig = plt.figure()
gs1 = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 1)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs1[0])
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs1[1])
example_plot(ax1)
example_plot(ax2)
gs1.tight_layout(fig)
您可以提供一個可選的 rect 參數,該參數指定子圖將要適合的邊界框。座標以標準化圖形座標表示,預設值為 (0, 0, 1, 1) (整個圖形)。
fig = plt.figure()
gs1 = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 1)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs1[0])
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs1[1])
example_plot(ax1)
example_plot(ax2)
gs1.tight_layout(fig, rect=[0, 0, 0.5, 1.0])
但是,我們不建議使用此方法手動建構更複雜的佈局,例如在圖形的左側和右側各有一個 GridSpec。對於這些用例,應該改為利用 巢狀 Gridspecs 或 圖形子圖。
圖例和註解#
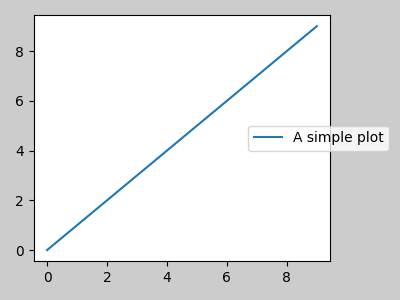
在 Matplotlib 2.2 之前,圖例和註解不包含在決定佈局的邊界框計算中。隨後,這些藝術家被添加到計算中,但有時不希望包含它們。例如,在這種情況下,最好稍微縮小軸的大小,為圖例騰出空間
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(4, 3))
lines = ax.plot(range(10), label='A simple plot')
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(0.7, 0.5), loc='center left',)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
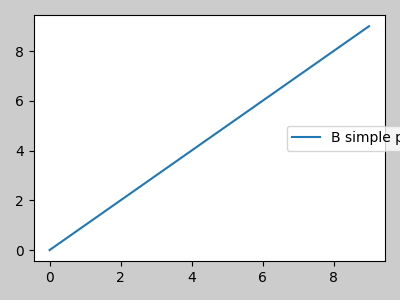
但是,有時不希望這樣做(當使用 fig.savefig('outname.png', bbox_inches='tight') 時通常如此)。為了從邊界框計算中移除圖例,我們只需設定其邊界 leg.set_in_layout(False),圖例將被忽略。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(4, 3))
lines = ax.plot(range(10), label='B simple plot')
leg = ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(0.7, 0.5), loc='center left',)
leg.set_in_layout(False)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
與 AxesGrid1 一起使用#
提供對 mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 的有限支援。
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import Grid
plt.close('all')
fig = plt.figure()
grid = Grid(fig, rect=111, nrows_ncols=(2, 2),
axes_pad=0.25, label_mode='L',
)
for ax in grid:
example_plot(ax)
ax.title.set_visible(False)
plt.tight_layout()
顏色條#
如果您使用 Figure.colorbar 建立顏色條,則建立的顏色條會繪製在子圖中,只要父軸也是子圖,因此 Figure.tight_layout 將會正常運作。
plt.close('all')
arr = np.arange(100).reshape((10, 10))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4))
im = plt.imshow(arr, interpolation="none")
plt.colorbar(im)
plt.tight_layout()
另一種選擇是使用 AxesGrid1 工具組明確建立用於顏色條的軸。
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable
plt.close('all')
arr = np.arange(100).reshape((10, 10))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4))
im = plt.imshow(arr, interpolation="none")
divider = make_axes_locatable(plt.gca())
cax = divider.append_axes("right", "5%", pad="3%")
plt.colorbar(im, cax=cax)
plt.tight_layout()
腳本的總執行時間: (0 分鐘 9.086 秒)